Knee pain
-Distinctive features of knee pain-
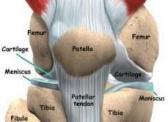
When you have knee pain, you find difficulties in walking and running and when it gets worse, you find difficulties in spending daily life. In order to improve QOL (quality of life), preventing from knee pain and betterment of knee pain is important. Types of so-called knee pain varies and require different treatments.
i) Osteoarthritis(OA)
Osteoarthritis is caused by degeneration of cartilage in the knee.OA causes a chronically painful knee that is often more painful with activity.
ii) Sprained and torn ligaments
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is the most commonly injured ligament in the knee. A force from the outer (lateral) knee to the inner (medial) knee is typically responsible for this injury.Severe ligaments sprains or tears often produce a tearing or ripping sensation along the inner joint line of the knee. You may also notice knee instability and swelling.
iii) Synovial capsule injury
Acute or overuse knee injuries may result in water on the knee. Swelling occurs as a result of leakage of fluid from damaged tissue.The damage within the knee joint irritates the joint lining (the synovium) and causes excess amounts of
synovial fluid to be produced.
(iv) Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease of the whole body that affects many joints often including the knee. Symptoms occurs in joints in both sides. In addition to knee pain, rheumatoid arthritis may produce morning stiffness and pain in
other joints.
v) Osgood-Schlatter disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease occurs in adolescent athletes where repetitive extension of the knee causes inflammation and injury of the tibial tubercle (of the bone itself).
The pain is typically worse when extending the leg. The tibial tubercle is tender to touch and over time begins to protrude more because the chronic inflammation stimulates the bone to grow.
vi) Patellofemoral syndrome and chondromalacia patella
These 2 conditions represent a spectrum of disease caused by patellar mistracking.The condition typically occurs in young women and also in athletes of both sexes and elderly people.In patellofemoral syndrome, the patella rubs against the inner or outer emur rather than tracking straight down the middle. As a result the patellofemoral joint on either the inner or outer side may become inflamed causing pain that is worse with activity or prolonged sitting. As the condition progresses, softening and decay of the articular cartilage on the underside of the patella occurs, and the syndrome is referred to as chondromalacia patella.
knee pain and Acupuncture
Large research initiative was conducted in year 2000 to determine efficacy, effectiveness, safety and cost effectiveness of acupuncture treatment in standard medical care. Evaluated a total of 304674 patients who received on average 10~13 acupuncture treatments for chronic pain (osteoarthritis of the hip or knee, low back pain, neck pain, headache) during a period of three months. Results and conclusions demonstrate that for the diagnoses examined, acupuncture in addition to usual care was an effective and safe treatment. As the conclusion shows acupuncture treatment for chronic pain is very effective.
In our acupuncture treatment, clinical condition is differentiated first, and we give a treatment for knee pain and at the same time we treat the muscle that trigger knee pain for protection.
Loss in strength or fatigue of quadriceps muscle or hamstring muscle (biceps femoris · semitendinosus · semimembranosus) often cause knee pain, hence we will approch those muscles for prevention as well.
Preventing knee pain
Prevention is also very important. Weight control, proper foot wear, keeping your knee warm, and moreover, developing quadriceps muscle is highly recommended.
The followings are knee exercises. Hope you will find them informative.
Quad Strengthening Contractions:
Sit in chair. Extend legs, heels to floor. Keep knees straight (or as straight as possible if you have arthritis.) Tighten thigh muscles. Hold for count of 10. Relax for count of 3. Do 10 repetitions. You can do this several times throughout the day. You can build up to 2 or 3 sets of 10 repetitions at a time.
Quad Strengthening Leg lifts:
Lie flat on back. Bend left knee at 90-degree angle, keeping foot flat on floor. Keeping the right leg straight, slowly lift it to the height of the left knee. Hold for a count of 3. Repeat 10 times. Switch sides. Work up to 10 sets of 10 over several weeks.
Safety Tip:
Leg lifts: Lifting both legs at the same time causes excessive stress on your lower back so
only lift one leg at a time; the opposite leg should be kept slightly bent with foot on floor.